openset-related-work
Problem
Open set recognition: Using K classes labels identify K+1 classes (1 as unknown).
Solutions
Selective Data
Use less data than the whole training set.
No Additional Data
Classification. No “unknown” samples generated.
OpenMax
OpenMax adapted EVT meta-recognition calibration in the penulimite layer of deep neural networks. For each instance, activation vector is revised to the sum of the product of its distance to the mean activation vectors (MAV) of each class. Then sent to softmax layer, which computes:
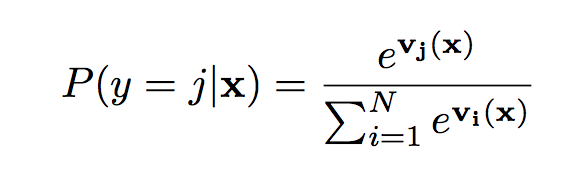
II-loss
ii-loss function was propsed in order to maximize the distance between different classes (inter class separation) and minimize distance of an instance from its class mean (intra class spread).
- intra class spread
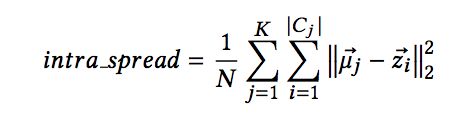
- inter class spread
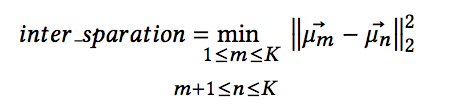
- ii-loss
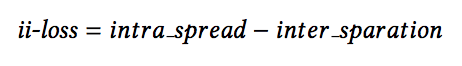
OSNN
The paper introduced two open-set extentions for the NN classifier: Class Verification (CV), as OSNN_cv and Nearest Neighbour Distance Ratio (OSNN). The difference is OSNN is able to classify test samples faraway from training ones while OSNN_cv does not.
Distribution Networks
The paper proposed distribution networks for open set learning, which can further recognize different novel classes rather than just one unknown class. It assumes every class follows a distinctive Gaussian distribution, thus likelihood was used in objective function. Meanwhile, to avoid imbalance class problem, the negative mean log likelihood was used for each class, and the final loss function looks like:
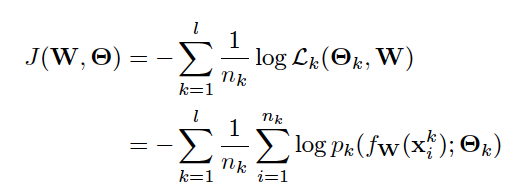
Where p_k denotes the Gaussian probability density function:
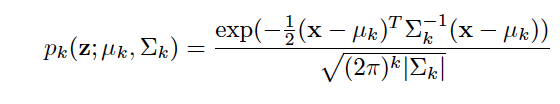
For each known class, If a test sample not belong any of the seen class, then the system would generate a new distribution for the novel class, whose parameters are estimated by a transfer strategy in validation process.
RLCN
The paper proposed a pairwise-constraint loss(PCL) function to achieve “intra-class compactness” and “inter-clas separation” in order to address openset recognition problem. They also developed a two-channel co-representation framework to detect novel class over time.
The overview of the RLCN framework looks like:
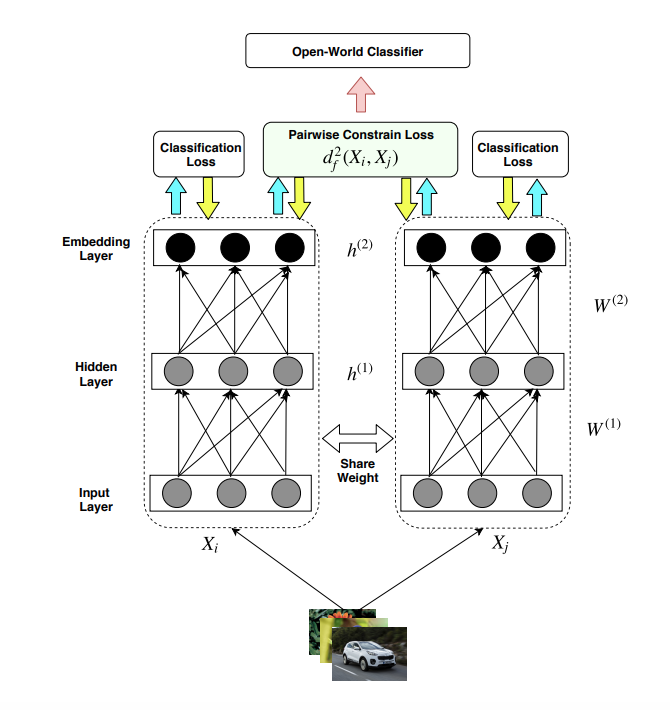
The paper proposed a pairwise constrain loss which looks like
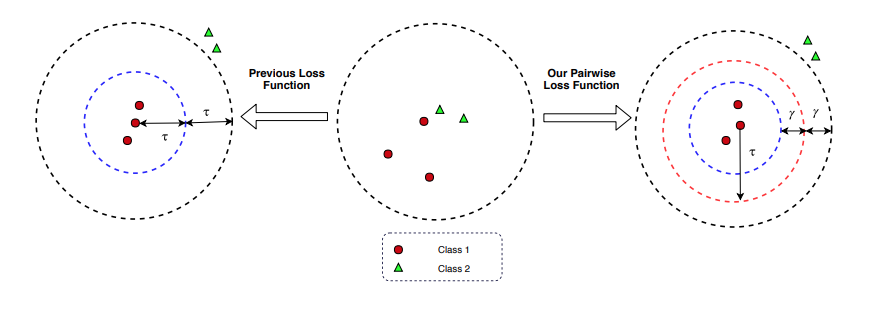
tao is a margin value and gamma is a constant range. The relationship between distance of two instances, tao and gamma looks like:
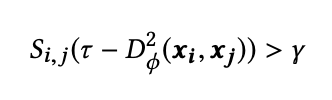
S_i,j measures the similarity between instances i and j, if i and j are similar, S_i, j = 1. Otherwise, if i and j are dissimilar, S_i, j = -1. The equation denotes that the inter-class distances should be at least (gammar + tao), and that for intra-class should be at most (tao - gammar).
To complete pairwise constrain, the paper also added an frobenius regularization term in order to avoid overfitting:
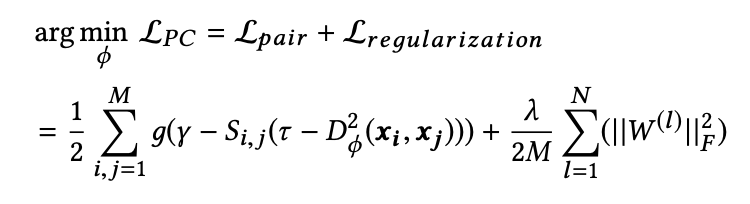
The model also applied binary classification error(BCE) at the final output layer, which looks like
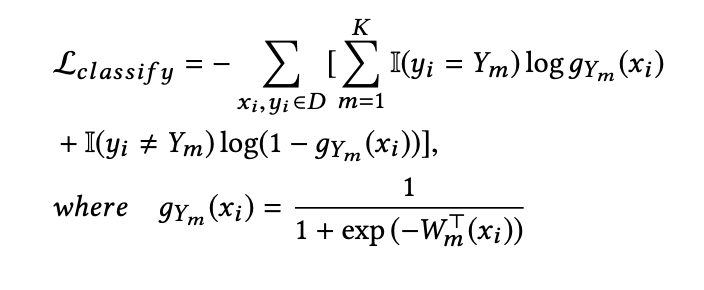
And the overall objective function of the network looks:
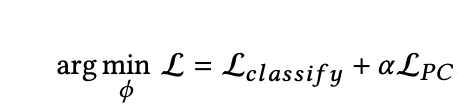
Generated Additional Data
Generate samples for “unknown” class first, then do classification.
G-OpenMax
Based on OpenMax and GANs, objective function as
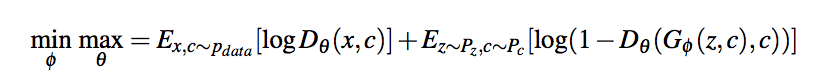
The function has an extra variable C than standard GANs, which denotes categories, which will be random selected as well: D(data, category). And there are K pre-trained classifier. For each generated sample, if the class with the highest value is different from the pre-trained classifier, it will be marked as “unknown”.
Adversarial Sample Generation
ASG also generates “unkown” samples, which are close to “known” samples, different from GANs minmax strategy, ASG generated samples who are: 1.close to the seen class data
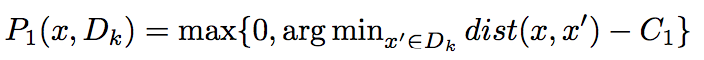
2.scattered around the seen/unseen boundary
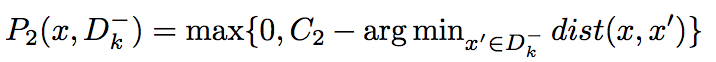
Hence in general,
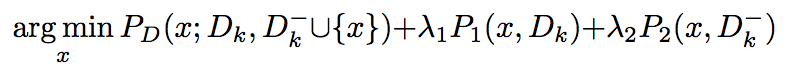
In the prediction stage, for a test instance x, if all “known” classifier are negative, x is predicted as “unkown”. Otherwise, x is predicted as the class with highest confidence.
Counterfactual Image Generation
Counterfactual image generation generates “unknown” samples around “known” samples. Different with standard GANs, the model uses an interpolated gradient penalty term P(D) to generate samples.
- minimize discriminator error
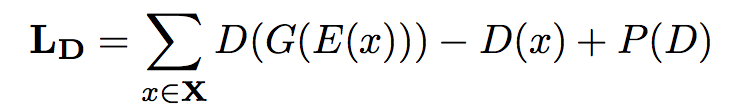
- minimize generator error
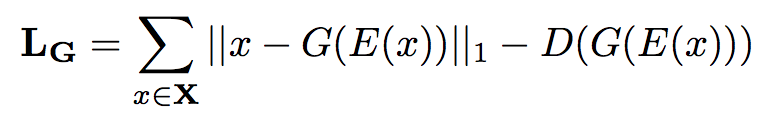
The architecture consists of three components: an encoder network E(x), a generator G(z) and a discriminator D. And the goal is to generate synthetic images closed to the real image but not in any k classes:
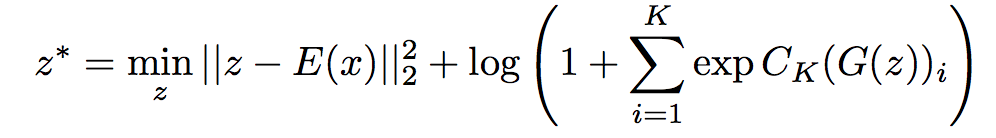
where z is the encoding of fake image, E(X) is the encoding of real image.
GAN-MDFM
The paper presented a new method to generate fake date in unknown class in generative adversarial networks(GANs) framework for open set recognition problem. The framework consists of one generator, one classifier, one feature extractor and two autoencoders who sharing their parameters. The classifier measures uncertainty about positive data and generated data. And its objective function looks like:
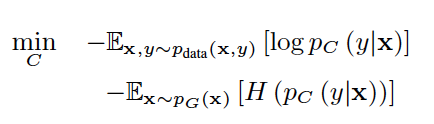
where H(p_c(y|x)) is the entropy of the membership probability.
The system intends to generate fake data close to feature space of positive data, thus the objective function looks like
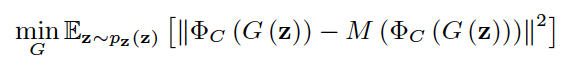
Being different from vanilla G, who models the distribution of known classes, the generator here models the distribution m away from that of known classes.
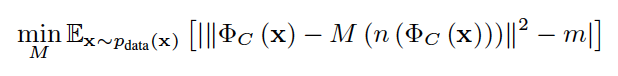
M(.) is introduced marginal denoising autoencoder (MADE) which “tries to model the noisy distribution of known classes on the feature space” of the classifier. And instead of adversarial loss, the objective function of autoencoder looks like: where n(.) is corruption function and m is a hyper-parameter to set the margin.
Introduced Additional Data
Introduce some other data than training set (not generated ones), then do classification.
Open Set Domain Adaptation by Backpropagation
The paper marked unlabeled target samples as unknown, then mixed them with labeled source samples together to train a feature generator and a classifier. The objective functions look like:
- classifier
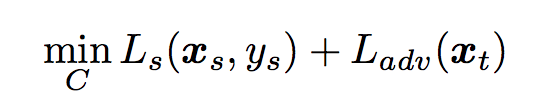
- generator
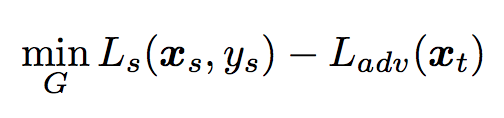
The classifier attempts to minimize both loss function whereas the generator attempts to maximize the value of L_adv(x_t) to deceive the classifier, such that it can generator better features which would recognize “known” samples from unlabeled target samples.
Unseen Class Discovery in Open-world Classification
The paper proposed a system which consists of three networks – an Open Classification Network (OCN), a Pairwise Classification Network (PCN), an auto-encoder, which introduced unlabeled data in auto-encoder training to avoid overfitting.
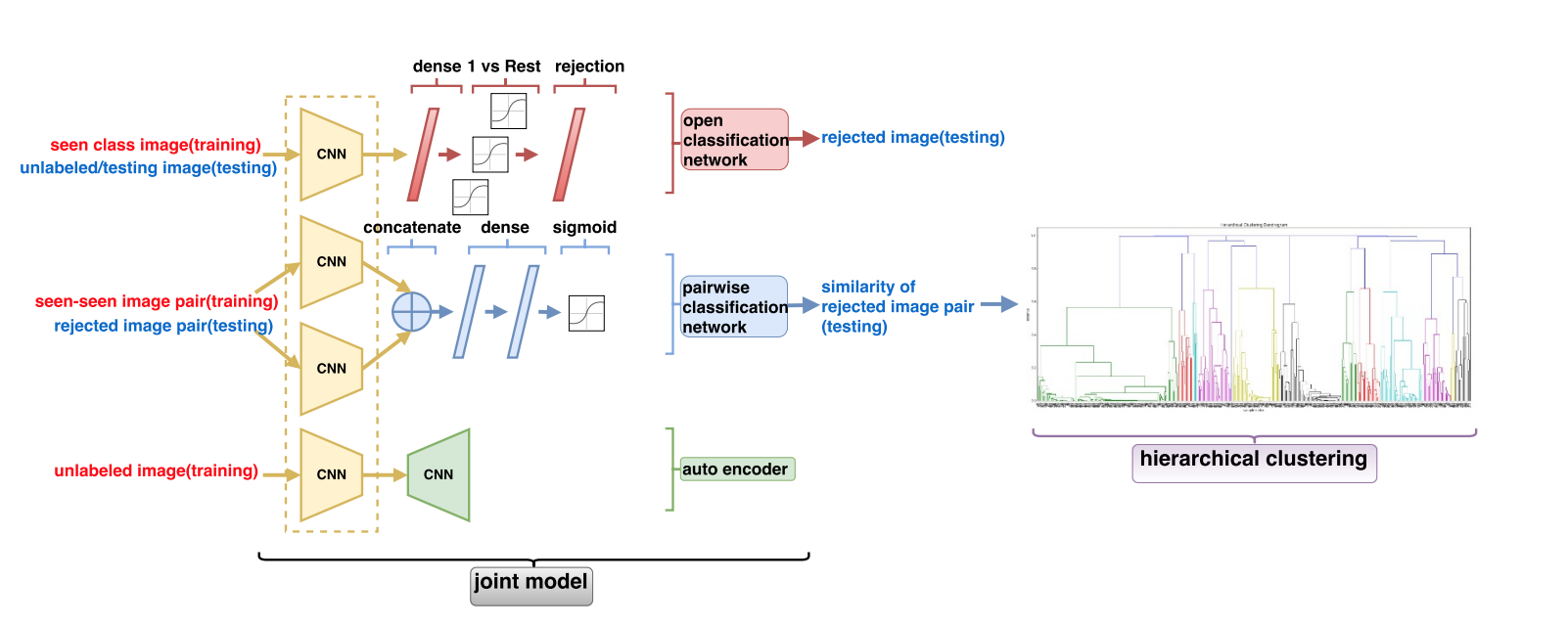
Unseen Class Discovery in Open-world Classification
Manual labeled unknown data is used in Open Deep Network (ODN). It introduces multiclass triplet thresholds to identify new categories: accept threshold, reject threshold and distance-threshold. Specifically, a samplewould be accepted as a labeled class if and only if the index of its top confidence value is greater than accept threshold. A sample would be considered as unknown if all the confidence values are below reject threshold. For samples between accept threshold and reject threshold, they would also be accepted as a labeled class if the distance between top and second maximal confidence values is large than the distance-threshold.
Outlier Exposure
OE borrowed data from other dataset to be “out-of-distribution” (OOD), denoted as D_out. Meanwhile target samples as “in-distribution”, marked as D_in. Then the model is trained to “discover signals and learn heuristics to detect” which dataset a query is sampled from.
Given a model f and the original learning objective L, the objective function of OE looks like
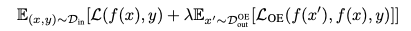
D_out_OE is outlier explosure dataset. The equation indicates the model tries to minimize the objective L for data from “in-distribution” (L) and “out-of-distribution” (L_OE). The paper also used maximum softmax probabilitybaseline dectector (cross-entropy) for L_OE. And when labels are not available, L_OE was set to a margin ranking loss on the log probabilities f(x’) and f(x).
Objectosphere Loss
The proposed method reduced the deep feature maginitude (||F(x)||) and maximize entropy of the softmax scores of unknown sample to separate them from known samples.
- Entropic Open-Set Loss
Enptropic open-set loss looks like
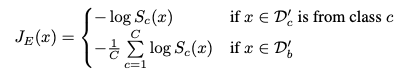
The idea is maximum entorpy when an input is unknown, which in hence should uniform probabilities over the known classes.
Compared with softmax and background method, we can see that unknown samples result in smaller output probabilities when usingobjectosphere loss.
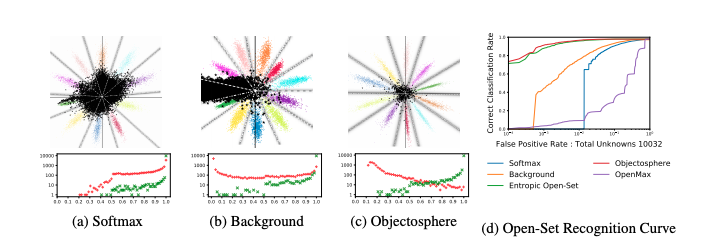
- Objectoshpere Loss
To further separate known and unknown samples, the paper pushed knownsamples into the “Objectosphere” where they have large feature magnitude and low entropy. And objectosphere loss is defined as
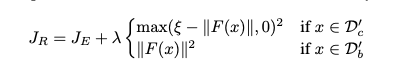
It penalizes the known classes if their feature maginitude is inside epsilon and unknown classes if their magnitude is greater than zero.
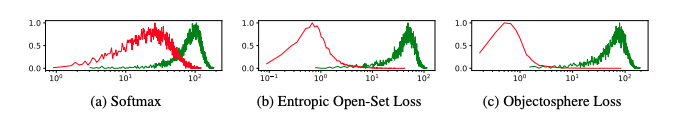
Deep Feature for One-Class Classification
The overview of proposed method looks like
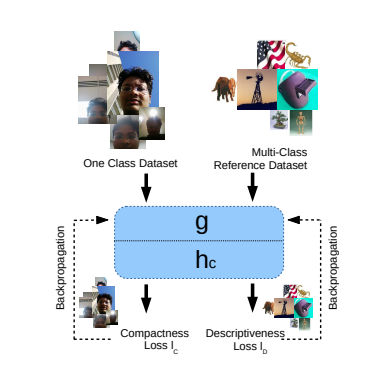
where g is feature extraction networks and h_c is classification networks. And the training and testing frameworks look like:
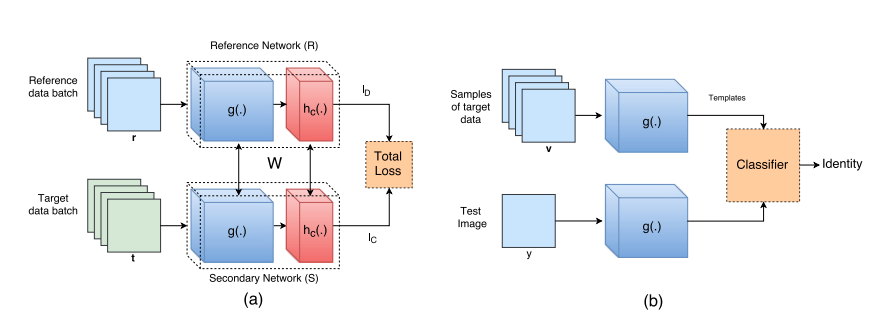
Reference network and secondary network are structually identical and also shared weights. l_D is the loss function (discriptive loss: cross-entropy) for reference dataset to distinguish different classes. l_C is the loss function (compactness loss) for second network to make samples from same class more compact. They used cross-entropy as discriptive loss here and compactness loss looks like:
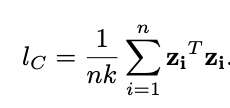
which is the average Euclidean distance between give sample and the rest of samples.